Science
Science underpins everything we do at Blue Forest
Swipe
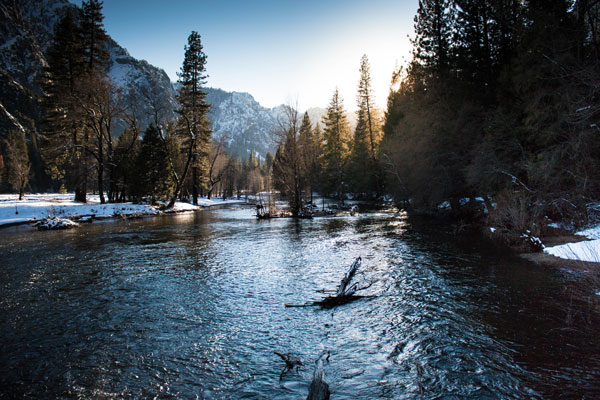
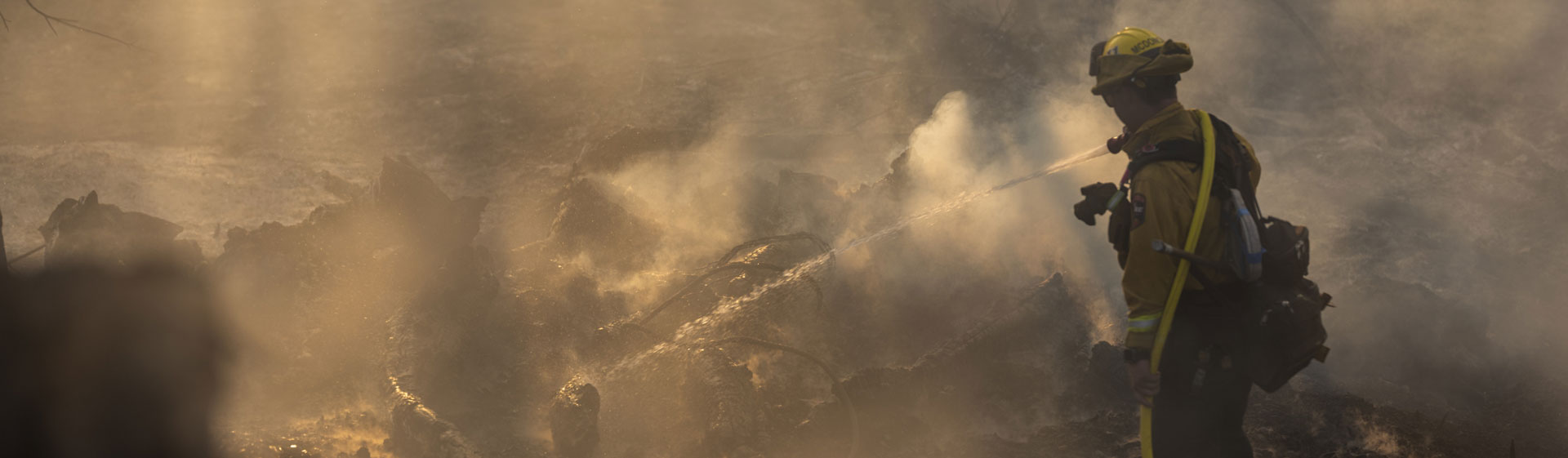
Tahoe National Forest

We combine the latest science with traditional knowledge and environmental restoration activities to build more resilient ecosystems and communities.
How ecosystem restoration works
Millions of acres of forest in the Western U.S. burn
catastrophically every year. And millions more are at
extreme risk.

Tahoe National Forest
That’s due, in part, to over a century of fire suppression.
When small, naturally occurring fires are suppressed, the forests we’re left with are denser than before. They have more trees, more bushes, more flammable material than would naturally occur.
If fire enters these overstocked forests, it’s catastrophic. We need to remove some of this flammable material so the forest can safely receive fire. And we also need to restore habitats, rivers, meadows, and other parts of the ecosystem.
We need to restore forests to how they were when Indigenous land stewards cared for them, to make them resilient to not just fire, but to insect outbreak, drought, and mortality. And we need to do it urgently as climate change brings additional challenges.
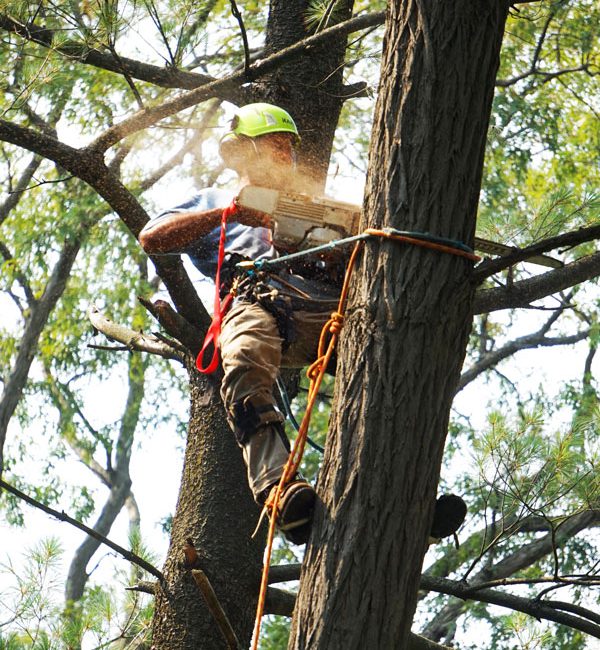
Ecological restoration work includes fuels reduction, removing trees by hand or machine, reintroducing beneficial fire, and activities like meadow restoration.
Key Benefits of Ecosystem Restoration
A resilient ecosystem has far reaching benefits for nature and communities, providing habitat, protecting water resources, and safeguarding infrastructure.
Key Benefits of Ecosystem Restoration
01. Biodiversity
Resilient ecosystems are characterized by varied species compositions and structures across a landscape
02. Wildfire Risk Reduction
Resilient forests are at decreased risk of high severity fire, protecting ecosystems, communities, and infrastructure from harm
03. Habitat Protection
Healthy ecosystems provide key habitat for a diverse range of animal species
04. Recreation
Healthy ecosystems support numerous outdoor recreation activities
05. Water Security
Resilient forests and ecosystems maintain clean and abundant water for human consumption, irrigation, industry, and power generation
06. Carbon Stability
Resilient forest ecosystems are less susceptible to high severity fire, reducing the emission of carbon stored in trees during a wildfire
07. Community Resilience
Resilient forest ecosystems protect communities from the impacts of high-severity, catastrophic wildfires
08. Economic Development
Restoration and maintenance of resilient forests and other ecosystems creates jobs and supports businesses through project implementation and wood products manufacturing
09. Public Health
Resilient forests and other ecosystems protect multiple aspects of public health, including reducing smoke exposure by lowering the risk of severe wildfire and protecting water quality
-
Biodiversity
-
Wildfire Risk Reduction
-
Habitat Protection
-
Recreation
-
Water Security
-
Carbon Stability
-
Community Resilience
-
Economic Development
-
Public Health
West Coast Fire Map
How we leverage science to help
Science is the backbone of our Forest Resilience
Bond projects.
Our science team works to evaluate and monitor project benefits. We help develop, test, and deploy new tools and methods for measuring restoration project outcomes.
We partner with academic and research organizations to evaluate and communicate the benefits of investing in ecosystem resilience.
And we maintain a portfolio of independent research projects aimed at gaining new insights into the benefits of well-managed landscapes.


